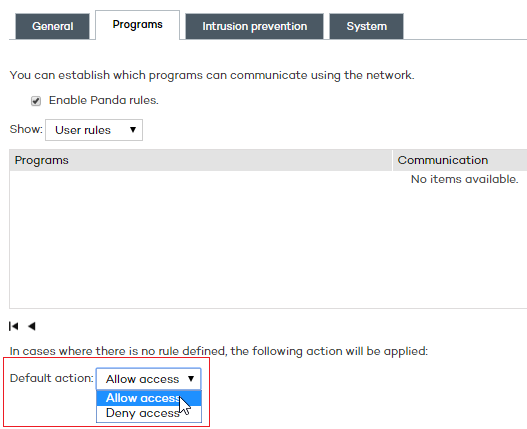
This tab allows administrators to specify which of the user's programs can communicate with the local network/Internet and which cannot.
To develop an effective protection strategy it is necessary to follow the steps below in the order listed:
Choose the default action:

Allow access: Allows communications for all programs with no specific rules assigned. This is the default, basic mode.
Deny access: Denies connections for all programs with no specific rules assigned. This is an advanced mode, as it requires adding rules for every frequently used program. Otherwise, those programs will not be allowed to communicate, affecting their performance.
Click Add to define the way a specific application should behave.
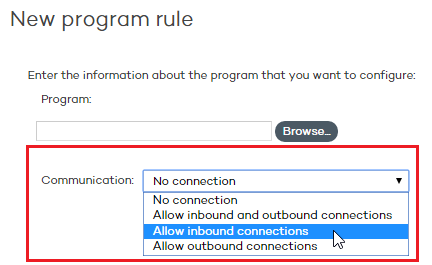
Allow inbound and outbound connections. The program can connect to the Internet/local networks and allows other programs or users to connect to it. There are certain types of programs that need these permissions to work correctly: file swapping programs, chat applications, Internet browsers, etc.
Allow outbound connections. The program can connect to the Internet/local networks, but won't accept inbound connections from other users or applications.
Allow inbound connections. The program accepts connections from programs or users from the Internet/local networks, but won't be allowed to establish outbound connections.
No connection. The program cannot connect to the Internet or local networks.
Related topics